All About Mandrel Bending
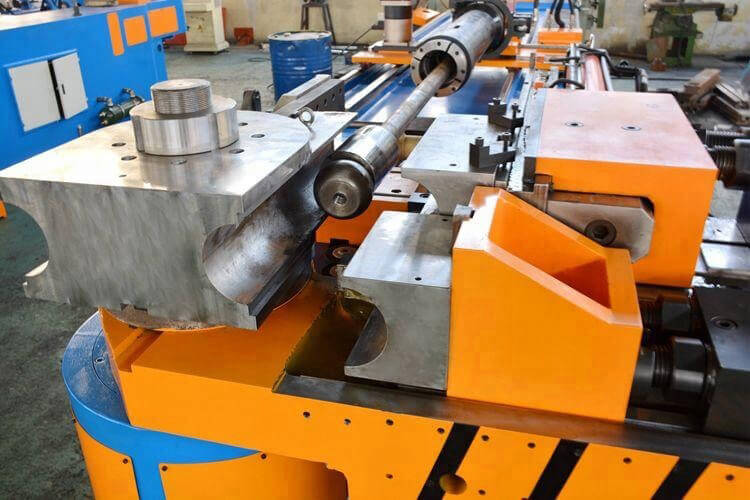

For tube and pipe bending, there are various ways and bending equipment on the market to achieve them bent. Today, we will talk about mandrel bending which is an advanced tube and pipe bending technology for high-quality, precise, and complex bending.
What is Mandrel Bending?
Mandrel bending is a specialized technique used to bend tubes and pipes into various shapes without any deformation. Mandrel is a solid or flexible rod that can be installed on various types of bending machines, and inserted into the tube or pipe while bending to maintain the integrity of the tube.
Key Components of Mandrel Bending
Related to mandrel pipe bending, there must be some key components worked together to achieve precise bending.
- Mandrel: An internal support can be designed for different types, such as a plug mandrel, a form mandrel, and a ball mandrel.
- Bending Die: A tool that is designed according to tube size and bending radius, used to form the desired shape and radius.
- Clamp Die: Hold the tube in place while bending.
- Pressure Die: Applies the necessary force to push the tube around the bending die.
- Wiper Die: Used to prevent wrinkles on the inside radius of the bend.
The Material of Mandrel and Pipe Bending Die
The material of the mandrel and pipe bending die needs to be customized according to different bending tube materials and applications. Below are the common materials and you can customize them from our engineer.
- Mandrel Materials: Steel, chrome, aluminum, or bronze mandrel.
- Pipe Bending Die Materials: Mold steel, 45# steel, chrome 12 molybdenum vanadium, copper alloy, nylon, and more.
The Importance of Mandrel Bending in Various Industries
- Automotive Industry: Used to bend exhaust systems, roll cages, and hydraulic lines, where precise bends are required.
- Aerospace Industry: Used to bend complex fuel lines, hydraulic systems, and structural components to meet stringent safety and performance standards.
- Shipbuilding: Used to bend pipelines and structural elements that require precise and reliable bending.
- Medical Devices: Used to manufacture precise and smooth bends in surgical instruments and medical tubing.
- Furniture and Architecture: Used to bend metal frames and decorative elements for the purpose of reasonable structure and beautiful appearance.
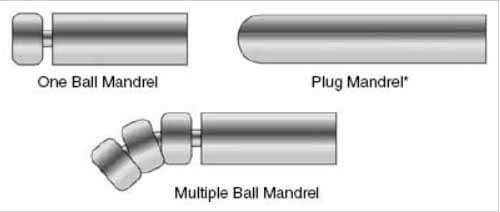
Types of Tube Bending Mandrels
Mandrel bending is a kind of bending technique, but there are various types of tube bending mandrels for different usages.
Plug Mandrel Bending
The plug mandrel is designed like a solid rod and used to insert into the tube to provide basic internal support while bending.
Pros of Plug Mandrel Bending
- Simple and cheap.
- Suitable for bends with larger radii.
- Easy to use and maintain.
Cons of Plug Mandrel Bending
- Limited support for tight bends.
- It may not prevent wrinkles or flattening in thin-walled tubes.
- Less effective for small-diameter tubes.
Applications of Plug Mandrel Bendig
- Used where precise bending is not critical.
- Suitable for bending thicker-walled tubes or pipes.
- Used in basic construction and industrial applications
Form Mandrel Bending
The form mandrel is designed like a solid rod with a curved end which could provide additional support to the inside of the tube and achieve the desired bend radius while bending.
Pros of Form Mandrel Bending
- Provides better internal support than plug mandrels.
- Reduces the risk of wrinkles and deformation.
- Suitable for tighter bend radii.
Cons of Form Mandrel Bending
- More complex and expensive than plug mandrels.
- Requires precise matching to the tube’s bend radius.
- Can be difficult to insert and remove in some cases.
Applications of Form Mandrel Bending
- Ideal for high-precision applications in the automotive and aerospace industries.
- Used in bending tubes with moderate radii.
- Suitable for situations where the interior surface quality of the tube is critical.
Ball Mandrel Bending
The ball mandrel consists of a series of spherical balls linked together, providing a flexible support inside the tube.
Pros of Ball Mandrel Bending
- Highly flexible and suitable for various bend radii.
- The best solution to support tight bends and thin-walled tubes.
- Minimizes the risk of wrinkles and deformation.
Cons of Ball Mandrel Bending
- More expensive and complex than other mandrel types.
- Requires careful setup and maintenance.
Applications of Ball Mandrel Bending
- Used in applications requiring tight bends and high precision, such as in medical devices and precision instruments.
- Suit for small-diameter tubes and complex bending shapes.
- Suitable for industries where high-quality interior surface finish is essential.
Sand Mandrel Bending
Sand mandrel bending means filling the sand into the tube before bending to support the internal of the tube to prevent collapse and deformation.
Pros of Sand Mandrel Bending
- Cheap and the material is easy to find.
- Can bend complex shapes.
- Suitable for a wide range of tube diameters and wall thicknesses.
Cons of Sand Mandrel Bending
- It takes a long time to set up and clean up.
- Not as precise and strong as other mandrel bending.
Applications of Sand Mandrel Bending
- Suitable for bending large-diameter tubes or pipes.
- Used in applications where specialized mandrels are not available or cost-prohibitive.
Mandrel bending also has a big difference compared to all other bending methods that without a mandrel, prevents springback of the material. The mandrel inside the tube can maintain the tube with its ideal shape.

How to Choose the Right Mandrel Type?
There are a few factors that will affect the mandrel type for mandrel bending, you need to consider the below points before purchasing.
Tube Material and Thickness
- Tube Material: Different materials (e.g., steel, aluminum, copper) have different levels of ductility and strength, impacting the choice of mandrel.
- Wall Thickness: Thin-walled tubes are more prone to collapse and require more support during bending.
Bend Radius and Complexity
- Bend Radius: Tighter bends require more sophisticated support to prevent deformation.
- Complexity of Bends: Complex shapes or multiple bends in close proximity may necessitate advanced mandrel types.
Desired Finish and Quality
- Surface Finish: High-quality internal and external finish requests also affect the mandrel type.
- Precision and Tolerance: High precision and minimal deviation will also need advanced mandrel support.
Please pay more attention that not only one factor will affect the choice of mandrel type, you need to comprehensively consider the above factors to ultimately determine the type of mandrel.
Not sure which mandrel bending type can meet your bending request? It is easy, our engineer will help you find the solution!
The Mandrel Bending Process
Here is the step-by-step process of mandrel tube bending.
Preparation and Setup
- Selection of Bending Tools: Select the mandrel type according to tube material, thickness, and bend radius.
- Machine Setup: Use the correct bending die, clamp die, pressure die and wiper die to set up the bending machine. Also need to make sure they are all in good condition.
- Tube Inspection: Inspect if any defect that will affect the bending result.
Insertion of the Mandrel
- Lubrication: Apply a suitable lubricant to the mandrel and the inside of the tube to reduce friction during bending.
- Insertion: Insert the mandrel into the tube carefully, and make sure it is positioned correctly and extends to the required length for support.
Bending the Tube
- Clamping: Using the clamp die to secure the tube in the bending machine to prevent movement during bending.
- Alignment: Make sure the tube is correctly aligned with the bending die to achieve the desired bend angle and radius.
- Bending Process: Initiate the bending process by rotating the bending die while the pressure die pushes the tube around the die. The mandrel provides internal support, preventing collapse and deformation.
Post-Bending Steps
- Mandrel Removal: Remove the mandrel from the bent tube after bending. Be careful not to damage the tube or mandrel.
- Inspection: Inspect whether there are any wrinkles, collapses, or deformation on the bent tube. Check the bending radius and bending angles.
- Clean: Clean the tube for the next procedure.

Advantages of Mandrel Bending
If you want to produce tube bending in a large scale, we strongly recommend you use mandrel bending, you will benefit a lot from this technique.
High Precision and High Quality
- High Precision: Mandrel bending provides a precise bend radius for each bend.
- Uniformity: Mandrel bending provides consistency for mass production.
Smooth Interior Surfaces
- Internal Support: The mandrel supports the interior of the tube during bending, preventing collapse and maintaining a smooth interior surface.
- Flow Efficiency: Smooth interior surfaces are very important for fluid flow.
Material Versatility
- Metal & Alloy Materials: Mandrel bending is effective for a variety of metal tubes, metal profiles, and metal solid bars. Such as stainless steel, iron, copper, brass, aluminum, titanium, etc.
Thickness and Diameter Considerations
- Thin-Walled Tubes: Bending thin wall tubes is always a challenge, but this type of tube bending task can be easily handled by using mandrel bending.
- Large and Small Diameters: Mandrel bending can proceed both on small-diameter tubes and large-diameter tubes.
Mandrel bending is the most common and popular method of bending metal tubes. This method can be used to bend metal tubes with the highest accuracy, the best quality, and the most perfect shape.
Are you looking for a mandrel bending machine? Contact TubeBenderN Today!

Denis Lau
Denis Lau has 20 years of work experience in the metal processing industry. His major in university was mechanical engineering, and after graduation, he started from the bottom of the workshop, gaining extensive hands-on professional experience and the ability to tackle challenges from various industries.


